Upload
xzaxarias1975
View
502
Download
7
Embed Size (px)
DESCRIPTION
Presentation in Powerpoint of M.B.A. Dissertation
Citation preview

HELLENIC OPEN UNIVERSITYSCHOOL OF SOCIAL SCIENCES
M.B.A. THESIS
FINANCIAL STATEMENT ANALYSIS AS A MEANS FINANCIAL STATEMENT ANALYSIS AS A MEANS FOR ASSESSING CORPORATE FOR ASSESSING CORPORATE
CREDITWORTHINESS AND VIABILITYCREDITWORTHINESS AND VIABILITY
ByBy
Christos ZachariasChristos Zacharias
Supervisor: Dr Dimitris PetmezasSupervisor: Dr Dimitris Petmezas

INTRODUCTION
Financial Statement Analysis is the examination of the relations among
various economic elements that are included in the published financial
statements of companies. It facilitates users (i.e. creditors, investors
etc) of them to make sound economic decisions.
Commercial Banks use financial statements to assess the current and
past financial position and performance of companies that apply for
credit and loans, in order to evaluate their capacity to repay debt and
to determine the amount of credit risk involved in a lending situation.

MOTIVATION & OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY
Recent examples of accounting scandals and bankruptcies (i.e.Enron) have
raised questions about the usefulness and adequacy of financial statements
in helping creditors and investors make sound economic decisions.
In addition, the recent international financial crisis has proved that the
underestimation of credit risk can have devastating consequences for
Financial Institutions (i.e. Lehman Brothers Bankruptcy).
This study attempts to evaluate the adequacy, effectiveness and predictive
ability of financial statement analysis as a means for assessing corporate
creditworthiness and financial viability from the viewpoint of Commercial
Banks as creditors.

METHODOLOGY AND DATA
Part A΄:
Examination of the theoretical framework for credit standing and viability
assessment of enterprises through financial statement analysis, including
presentation of business failure predictions models, by reviewing the
relevant literature.
Part B΄:
Empirical investigation: We assess the credit standing and viability of a
sample of 10 publicly traded Greek companies, which have been manually
collected from A.S.E. More specifically, we make comparative analysis
between 5 financially healthy and 5 financially unhealthy companies of the
same industries, by using a failure prediction model and some financial
ratios.

THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK (1)
Presentation of objectives (according to various points of view) and most
common methods of financial statement analysis:
• Comparative Financial Statement Analysis
• Common - Size Financial Statement Analysis
• Ratio Analysis
• Cash Flow Analysis

THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK (2)
Presentation of the assessment of corporate creditworthiness and financial
viability, from the viewpoint of Commercial Banks, in the general context of
business credit approval process and credit risk evaluation:
I.Business and industry risk assessment
II.Analysis of financial performance and financial ratios
i. Analysis of Liquidity
ii. Analysis of Solvency & Capital Structure
iii.Analysis of Profitability
iv.Analysis of Efficiency
→

THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK (3)
III. Analysis and forecasting of cash flows
IV. Analysis of non-financial indicators (evaluation of quality criteria like
collateral and business character)
V. Credit decision making

THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK (4)
Examination of the use of financial ratios for predictive purposes and review of
the most popular classical statistical business failure prediction models which
are based on financial statements and especially on financial ratios:
Univariate Analysis (W.Beaver)
Multivariate Discriminant Analysis Models (Z-Score and ZETA models)
Conditional Probability Models (Logit and Probit Analysis)

THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK (5)
Presentation of the most important limitations in financial statement analysis
and their consequences on corporate credit analysis:
General Limitations
Historical Cost Principle
Contingent Liabilities
Accounting Risk
Proportionality of Financial Ratios
Creative Accounting

EMPIRICAL INVESTIGATION (1)
Comparative analysis between 5 financially healthy publicly traded companies
and 5 financially unhealthy/ failed ones of the same industries, by using a
failure prediction model (Altman’s Z-score) and 5 financial ratios which are
considered important in corporate credit analysis.
(Companies whose shares were recently suspended were selected as examples of
unhealthy companies. Companies whose shares were not suspended nor were under
observation were selected as examples of non-failed (healthy) companies.)
The selected financial ratios and Z-score are comparatively examined in pairs
of companies that belong to the same sector for testing whether these ratios
and Z-score of failed companies are significantly different to those of non-failed
ones in the years before failure and whether they are good indicators of
corporate creditworthiness and viability.

EMPIRICAL INVESTIGATION (2)
Altman’s Z-score model was selected as it is one of the most popular M.D.A. models for
predicting business failure. The discriminant function of this model (applicable to
publicly traded companies) is the following:
where:
X1 = Net Working capital /Total assets
X2 = Retained Earnings /Total assets
X3 = Earnings before interest and taxes /Total assets
X4 = Market value of equity /Book value of total debt
X5 = Sales /Total assets
In this model, a Z score of above 2.99 indicates non-failure, and a Z score below 1.81
indicates potential failure.
Z-score = 1.2(X1) + 1.4(X2) + 3.3(X3) + 0.6(X4) + 1.0(X5)
EMPIRICAL INVESTIGATION (3)
The financial ratios which have been selected for the comparative analysis are the
following (The financial data which ratios are derived from cover the period of 2004 –
2010) :
a) Debt Payback ratio or Cash Debt Coverage ratio (Operating Cash Flow / Total
Debt)
b) Return on Total Assets ratio - R.O.A. (Earnings Before Interest and Taxes / Total
Assets)
c) Equity Capital to Total Debt ratio (Owner’s Equity / Total Debt)
d) Debt Service Coverage ratio (Earnings before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation and
Amortization / Interest expense + Principal payments / (1-tax rate) )
e) Times Interest Earned ratio (Net Profit Before Taxes + Interest Expense / Interest
Expense)

EMPIRICAL INVESTIGATION (4)
The pairs of healthy and unhealthy companies that were selected are the following:
A.SPACE HELLAS S.A. & MARAC ELECTRONICS S.A. (Subsector:
Telecommunications Equipment)
B.F.G. EUROPE S.A. & EMPORIKOS DESMOS S.A. (Subsector: Durable
Household Products)
C.DAIOS PLASTICS S.A. & PETZETAKIS S.A. (Subsector: Specialty Chemicals)
D.“ALFA-BETA" VASSILOPOULOS S.A. & ATLANTIK SUPER MARKET S.A.
(Subsector: Food Retailers & Wholesalers)
E.KARAMOLENGOS BAKERY INDUSTRY S.A. & C.CARDASSILARIS & SONS –
CARDICO S.A. (Subsector: Food Products)

EMPIRICAL INVESTIGATION (5)
Comparative analysis between the 2 groups of companies: The averages of the
5 selected ratios & Z-score of the two categories of companies (healthy and
unhealthy) are compared between them.
Diagram 1 : Development of average Z-score values for healthy and unhealthy companies

EMPIRICAL INVESTIGATION (6)
Diagram 2 : Development of average Debt Payback ratio values for healthy and unhealthy companies
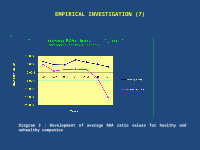
EMPIRICAL INVESTIGATION (7)
Diagram 3 : Development of average ROA ratio values for healthy and unhealthy companies
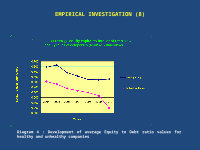
EMPIRICAL INVESTIGATION (8)
Diagram 4 : Development of average Equity to Debt ratio values for healthy and unhealthy companies
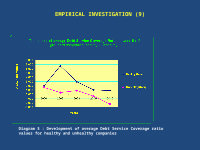
EMPIRICAL INVESTIGATION (9)
Diagram 5 : Development of average Debt Service Coverage ratio values for healthy and unhealthy companies
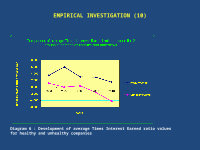
EMPIRICAL INVESTIGATION (10)
Diagram 6 : Development of average Times Interest Earned ratio values for healthy and unhealthy companies

EMPIRICAL INVESTIGATION (11)
Most Important Findings and Conclusions :
The two groups of companies have significantly different Z-score values, during
all years of the period under consideration.
3 out of 5 ratios of failed companies present significant differences to those of
non-failed ones in four years before failure.
The distinct examination of individual ratios does not lead to clear conclusions
regarding the corporate credit standing and viability.
The joint analysis of some financial ratios which contain common informative
characteristics (i.e. Solvency ratios) can lead to a correct prediction of
companies’ creditworthiness and future financial position.
The overall predictive ability of Z – score model is moderate.

EMPIRICAL INVESTIGATION (12)
Most Important Findings and Conclusions (continuity):
During the last 3 years (2008, 2009 and 2010), of the period under review,
Z-score values, both in company level and on average, are generally very
low, compared with the corresponding values of the previous 4 years.
Therefore, we can conclude that the emergence of unforeseen troubles in
the international and domestic macroeconomic business environment
affects negatively the reliability of Z-score model in terms of correct
classification of companies.

GENERAL CONCLUSIONS
Generally, the analysis of reliable financial statements is fairly effective on the
proper assessment of companies’ creditworthiness and the prediction of their
viability made by Commercial Banks. On the other hand, this analysis is subject
to certain limitations, due to the inherent weaknesses of financial statements,
and cannot provide a complete understanding of the borrowing companies.
Therefore, financial statement analysis is not sufficient, so that to lead by itself
Loan Officers to make final credit decisions. However, it constitutes a very
useful and indispensable tool within the business credit approval process that is
followed by Commercial Banks.

THANK YOU FOR YOUR ATTENTION